What is CHD?
All muscles in the body require a energy to function. The energy is provided by the supply of oxygen from circulating
blood. The heart is also made up of muscle, referred to as cardiac muscle. Coronary Arteries are the blood vessels that
supply blood to the cardiac muscles.
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also known as Ischaemic Heart Disease or Coronary Artery Disease, is a condition of
the heart when the flow of blood through the coronary arteries become reduced.
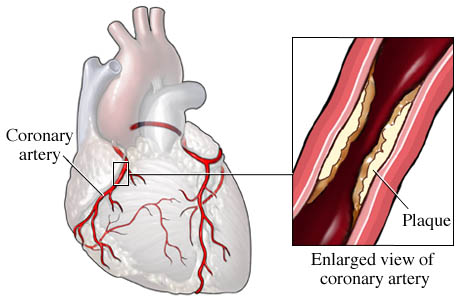
Narrowing of the coronary arteries is primarily caused by the build-up of a lipid based based plaque (atheroma) in the
walls. This process of plaque development is known as atherosclerosis.
The narrowing causes an insufficient supply of oxygen to cardiac muscles. Angina is the pain felt when the cardiac
muscles struggle to function as a result of this.
Sometimes a clot may form causing a complete blockage of a coronary artery. In this case, the cardiac muscle cells may
die which leads to a heart attack (Myocardial Infarction).
Of course, this doesn't develop randomly. There are factors which increase the risk and contribute to the
formation of plaque in the arteries, all of which is discussed in other pages on this site.
References [Show/Hide]

Royal Free & UCL Medical School
